Secure Boot State Unsupported? Here’s What It Means
3 min read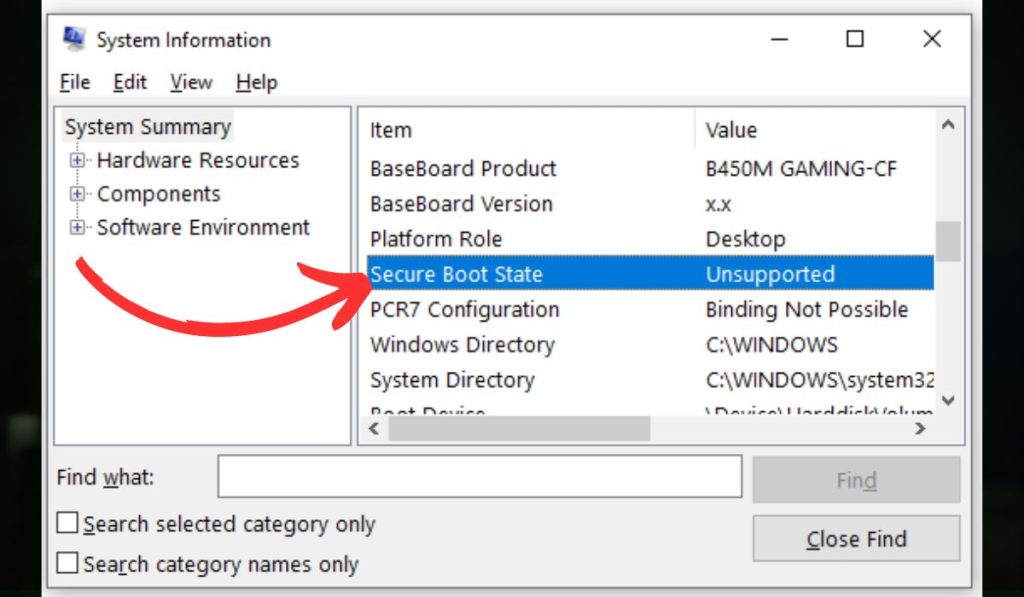
When diving into your system’s security settings or attempting to upgrade to a newer operating system like Windows 11, you might stumble upon the message: “Secure Boot State: Unsupported.” To many users, this can be a confusing and somewhat alarming message. But don’t panic just yet. This article will guide you through what this term means, why it may appear, and what steps you can take to address it.
What Is Secure Boot?
Secure Boot is a security standard developed by members of the PC industry to ensure that a device boots using only software that is trusted by the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM). It is part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and helps prevent malicious software from loading when a system starts.
When Secure Boot is enabled and configured correctly, it can protect against rootkits and bootkits—powerful types of malware that can attack your system before the operating system loads.

What Does “Secure Boot State: Unsupported” Mean?
Seeing the phrase “Secure Boot State: Unsupported” essentially means one of two things:
- Your PC does not support Secure Boot because it uses legacy BIOS rather than UEFI.
- Secure Boot is not available or disabled due to hardware, firmware, or settings issues.
In simpler words, it’s a status report indicating that the Secure Boot feature is not currently active or accessible on your device, either because the system doesn’t support it at all or because it’s turned off in the firmware settings.
Probable Reasons Behind Secure Boot Being Unsupported
- Legacy BIOS Mode: Your system is using old BIOS instead of UEFI.
- MBR Partition Style: Secure Boot requires the disk to use GPT (GUID Partition Table) instead of MBR (Master Boot Record).
- UEFI Settings Disabled: Secure Boot might be disabled in the UEFI firmware settings.
- Outdated Firmware: Some systems may need a firmware update to fully support Secure Boot.

How to Check Secure Boot Status
To see your system’s Secure Boot status in Windows:
- Press Windows Key + R, type msinfo32, and hit Enter.
- In the System Information window, look for Secure Boot State on the right side.
If it says “Unsupported”, proceed to analyze whether your system uses BIOS or UEFI and check the partition style.
Can Secure Boot Be Enabled?
In most cases, yes—if your hardware supports it. Here’s a general outline to enable Secure Boot:
- Enter your UEFI firmware settings (usually by pressing F2, DEL, or ESC upon boot).
- Look for the Secure Boot option and set it to Enabled.
- Ensure that the system is in UEFI boot mode (not Legacy/CSM).
- Verify that your drive uses GPT partition style. You may need to convert it from MBR to GPT.
Note: Changing from Legacy to UEFI, and converting MBR to GPT, could affect your existing data. Always back up important files before making adjustments.
Why Is Secure Boot Important?
Secure Boot plays a vital role in enhancing system security. By only allowing trusted code at boot time, it helps maintain the integrity of the operating system. It’s especially important in corporate and enterprise settings or for users planning to upgrade to Windows 11, which requires Secure Boot to be enabled.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can I install Windows 11 without Secure Boot?
A: Technically, yes, using workarounds, but Microsoft recommends Secure Boot for full compatibility and security. -
Q: Is Secure Boot the same as TPM?
A: No, Secure Boot verifies boot integrity, while TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a hardware chip that helps with encryption and security processes. -
Q: What happens if I enable Secure Boot?
A: Your system will verify the OS loader before booting. If the loader isn’t signed or recognized, booting will fail with a warning or error. -
Q: Will enabling Secure Boot erase my data?
A: No, enabling Secure Boot won’t erase data, but switching from Legacy BIOS to UEFI might require a drive format or partition style change. -
Q: How do I know if my system supports Secure Boot?
A: Check via msinfo32 or look up your motherboard’s features in its specification manual.
Understanding Secure Boot and its implications can help users better navigate system configurations and prepare for important upgrades. Whether you’re a casual user or an IT professional, ensuring that your hardware supports Secure Boot and is properly configured offers a critical boost to system security.